On July 23, 2024, the Union Minister of Finance and Corporate Affairs, Shrimati Nirmala Sitharaman, presented the Union Budget 2024-25 in Parliament. Here are the key highlights of the budget presented by her.
PM Modi said in x post that budget is for Viksit Bharat:
The #BudgetForViksitBharat ensures inclusive growth, benefiting every segment of society and paving the way for a developed India.https://t.co/QwbVumz8YG
— Narendra Modi (@narendramodi) July 23, 2024
Budget Estimates 2024-25
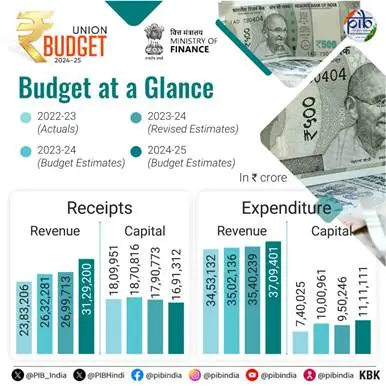
The budget estimates for 2024-25 include total receipts other than borrowings amounting to INR 32.07 lakh crore. The total expenditure is projected at INR 48.21 lakh crore. The net tax receipt stands at INR 25.83 lakh crore. The fiscal deficit is 4.9% of GDP. The government aims to reduce the deficit to below 4.5% next year. Inflation remains low and stable, moving towards the 4% target, with core inflation at 3.1%.
The government’s focus on managing the fiscal deficit and keeping inflation low demonstrates a commitment to economic stability. The target is to bring the deficit below 4.5% next year. This is a very ambitious target, but it is necessary for sustainable growth.
Focus on Employment, Skilling, MSMEs, and the Middle Class
A significant focus of the budget is on employment, skilling, MSMEs and the middle class. A package of five schemes under the Prime Minister’s initiative aims to provide employment and skilling opportunities to 4.1 crore youth. This will be provided over a five-year period.
This focus on employment and skilling is crucial for addressing the unemployment issue and boosting the capabilities of the workforce. This can lead to increased productivity and economic growth.
Prime Minister’s Package of Five Schemes
The Prime Minister’s package includes:
- Scheme A: First Timers: Provides up to INR 15,000 in three installments to first-time employees registered with the EPFO.
- Scheme B: Job Creation in Manufacturing: Offers incentives to employees and employers regarding their EPFO contributions for the first four years.
- Scheme C: Support to Employers: Government reimburses up to INR 3,000 per month for two years towards EPFO contributions for each additional employee.
These schemes are designed to incentivize job creation and support new employees. Especially in the manufacturing sector, jobs will be created which is essential for economic growth and employment.
New Centrally Sponsored Scheme for Skilling
A new centrally sponsored scheme aims to skill 20 lakh youth over five years. 1,000 Industrial Training Institutes (ITIs) will be upgraded in a hub and spoke arrangement.
By this, they will enhance the skill set of the youth which is vital for meeting the demands of a modern economy and improving employability.
New Scheme for Internships
A new scheme will offer internships in 500 top companies to 1 crore youth over five years. They will provide internships in top companies. This will give youth valuable industry experience and improve their job prospects.
Nine Budget Priorities for ‘Viksit Bharat’
The budget outlines nine priorities to achieve a developed India (‘Viksit Bharat’):
- Productivity and resilience in agriculture
- Employment and skilling
- Inclusive human resource development and social justice
- Manufacturing and services
- Urban development
- Energy security
- Infrastructure
- Innovation, research, and development
- Next-generation reforms
These priorities cover a broad spectrum of sectors essential for comprehensive and balanced economic development.
Priority 1: Productivity and Resilience in Agriculture
An allocation of INR 1.52 lakh crore is made for agriculture and allied sectors. New high-yielding and climate-resilient crop varieties will be released, and 1 crore farmers will be introduced to natural farming.
Investing in agriculture and introducing resilient crop varieties are crucial steps towards sustainable farming and food security.
Priority 2: Employment & Skilling
Schemes for employment linked incentives, establishment of working women hostels and women-specific skilling programs are announced in the budget.
These initiatives aim to increase women’s participation in the workforce. By this, they will support overall employment and skill development.
Priority 3: Inclusive Human Resource Development and Social Justice
Key projects include the development of industrial nodes, power projects and special financial support to states under various schemes.
These projects aim to promote regional development and address social justice issues. This ensures inclusive growth.
Priority 4: Manufacturing & Services
Various schemes to support MSMEs will be provided. This includes introduction of a credit guarantee scheme, enhanced Mudra loans and financial support for food irradiation units.
Supporting MSMEs is vital for economic growth. They are significant contributors to employment and GDP.
Priority 5: Urban Development
Plans include transit-oriented development, investment in urban housing and support for street markets.
Urban development initiatives are necessary to accommodate the growing urban population and improve living standards.
Priority 6: Energy Security
Policies for energy transition, promoting pumped storage projects, and partnering with the private sector for nuclear energy R&D are highlighted.
Ensuring energy security through diverse and sustainable sources is crucial for long-term economic stability.
Priority 7: Infrastructure
The budget allocates INR 11,11,111 crore for capital expenditure on infrastructure and INR 1.5 lakh crore for state governments to support infrastructure investment.
Investing in infrastructure is essential for economic growth and improving connectivity and services.
Priority 8: Innovation, Research & Development
An Anusandhan National Research Fund and a financing pool for private sector-driven research and innovation are proposed.
Promoting R&D and innovation is key to maintaining competitiveness and fostering technological advancements.
Priority 9: Next Generation Reforms
Reforms include digitization of land records, integration of job portals and a new pension plan for minors. Implementing next-generation reforms will streamline processes, enhance efficiency and provide better services to citizens.
The Union Budget 2024-25 presents a comprehensive plan to address various sectors of the economy. They are specially aiming for sustainable and inclusive growth.
About the Author
Mr. Radhesh Tarang Shah, is a management student at Institute of Management, Nirma University. He has a passion for writing articles and poems. He has experience as a financial analyst, author, news writer, marketer and social worker.